Recent advancements in quantum physics have uncovered a fascinating link between the transmission of energy and information across interfaces of diverse quantum field theories. Published in the esteemed Physical Review Letters on August 30, a study spearheaded by a collaborative team, including Hirosi Ooguri and Fred Kavli, provides a refreshing perspective on the long-standing complexities associated with these interfaces in both particle physics and condensed matter research. This work could very well be a game changer, offering a pathway to a deeper understanding of fundamental quantum processes.
The Central Findings
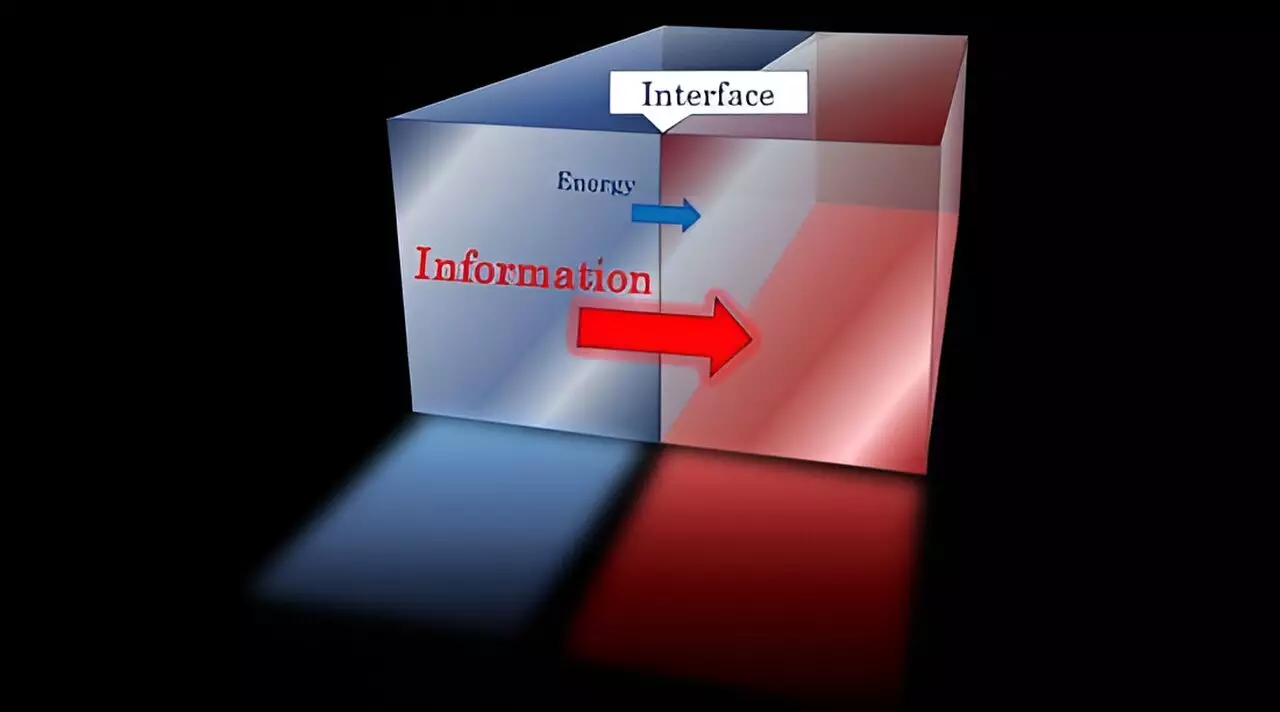
What makes this research particularly intriguing is the researchers’ discovery of a simple yet profound relationship: universal inequalities that connect three pivotal quantities—energy transmission rates, information transmission rates, and the size of the Hilbert space. In their analysis of two-dimensional theories characterized by scale invariance, they established the inequality [energy transmittance] ≤ [information transmittance] ≤ [size of Hilbert space]. This relationship indicates that effective energy transport is inherently tied to information transfer, establishing a foundational principle that energy flow cannot occur devoid of informational context.
This discovery not only simplifies the understanding of energy and information dynamics but also introduces restrictions on their interactions. Energy cannot simply race ahead without the necessary backdrop of information transfer and an adequate supply of states from Hilbert space to facilitate the process. This revelation holds significant implications for our theoretical frameworks and may pave the way for innovative computational models.
Why This Matters
One of the more compelling aspects of this research is its dual relevance to both theoretical physics and practical applications. The implications of this inequality extend beyond abstract physics; understanding how energy and information interplay can lead to advancements in quantum computing and communications technologies. In an era where information technology drives societal progress, the linkage between information transfer and energy use could inform the design of more efficient computational systems.
Moreover, the clarity provided by these established inequalities can guide further research into quantum field theories, an area that has often been riddled with complex calculations and ambiguous interpretations. By cementing the relationship between energy and information, the researchers have not only carved out a new avenue of inquiry but have also equipped future scientists with a foundational principle that can be tested and explored further.
Implications for Future Research
The paper’s assertion that no stronger inequality exists between these quantities presents an important challenge for physicists: how to utilize this understanding to probe deeper into quantum mechanics. Future inquiries may focus on expanding these inequalities beyond two-dimensional theories or seeking other contexts in which they apply. Researchers might examine how variations in the structure of the Hilbert space could affect energy and information dynamics, or how these principles can be harnessed in new technologies.
The exploration of the relationship between energy and information transmission in quantum field theories represents a significant leap forward in our comprehension of the universe’s underlying mechanics. With this foundation, physicists are poised to unlock further mysteries that dwell at the quantum level.