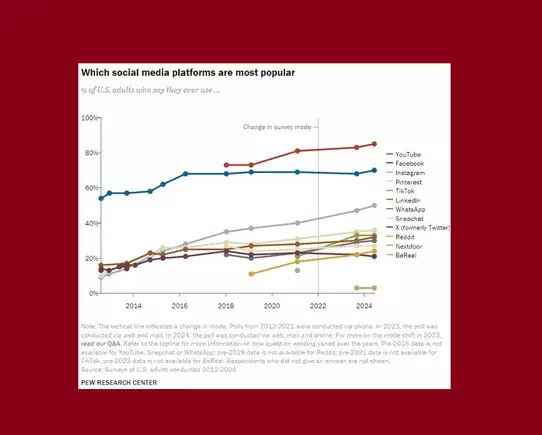
Recent data released by Pew Research highlights significant trends within the realm of social media usage, particularly among U.S. adults. With a sample size of 5,626 individuals surveyed between February and June of the current year, the findings reflect an informative snapshot of where adults engage online. This comprehensive study reveals YouTube as the dominant platform, primarily due to its multifaceted content delivery, even though it may not fit neatly into the conventional category of social networking sites. Following closely behind are Facebook and Instagram, illustrating the continued relevance of established platforms in an increasingly fragmented social media environment.
According to the research, YouTube and Facebook lead the pack as the most commonly utilized platforms among U.S. adults. Notably, half of those surveyed report regular use of Instagram, marking it as a key player in the social media game. Conversely, emerging networks such as TikTok, LinkedIn, X (previously Twitter), and Snapchat demonstrate varying levels of engagement. Intriguingly, while TikTok showed promise as a rapidly growing contender, its recent stability in usage brings up questions regarding its long-term appeal. Similarly, Pinterest’s usage has seen an uptick, signaling that niche platforms may still carve out dedicated viewer segments in the crowded space.
While the report offers a quantifiable overview of platform popularity, it falls short of addressing the critical metric of time spent on each application. Understanding user engagement through time allocation could afford deeper insights into which platforms foster meaningful interactions. Reports suggest that TikTok users tend to spend significantly more time on the app compared to older platforms like Facebook. This discrepancy indicates not just a difference in user volume, but also in engagement quality, potentially altering marketing strategies for brands targeting specific demographics.
Demographic analysis from the Pew survey provides clarity on which age groups gravitate toward which platforms. Facebook remains a staple among older audiences, reinforcing its reputation as a haven for more mature social interactions. Conversely, TikTok and Snapchat cater predominantly to younger users, attracting the elusive Gen Z and millennial demographics. Strikingly, YouTube transcends age barriers, appealing to a wide audience, yet its primary function as a video-sharing platform raises questions about its categorization as a ‘social’ network. The parallel between user behaviors on TikTok and Instagram aligns with evolving definitions of social interactivity, suggesting a shift toward visual and video-centric content as quintessential in modern engagement.
One of the more intriguing facets of this research points to the fate of X (formerly Twitter), which has not experienced the drastic decline some expected. Rather, its usage demonstrates a subtle decline, indicating that it retains a place in the social media hierarchy. This highlights a crucial aspect of user loyalty and attachment; even facing new challengers, platforms can endure fluctuations as long as their core user base remains engaged.
As digital landscapes continually evolve, understanding these trends becomes essential for anyone aiming to engage audiences effectively. Marketing efforts identified with a robust social media strategy should be framed around these insights; knowing where and how audiences interact will shape outreach efforts moving forward. Utilizing data from platforms like Pew Research equips marketers and content creators with the tools necessary to avoid missteps and align their presence with user preferences effectively.
The 2023 Pew Research report not only sheds light on current social media usage trends but also raises pertinent questions about user engagement and platform relevance. As new platforms emerge or evolve, traditional giants must adapt to stay relevant, paving the way for innovative approaches to audience interaction and content delivery. The future of social media promises to be exciting, driven by the very consumers who shape its direction.