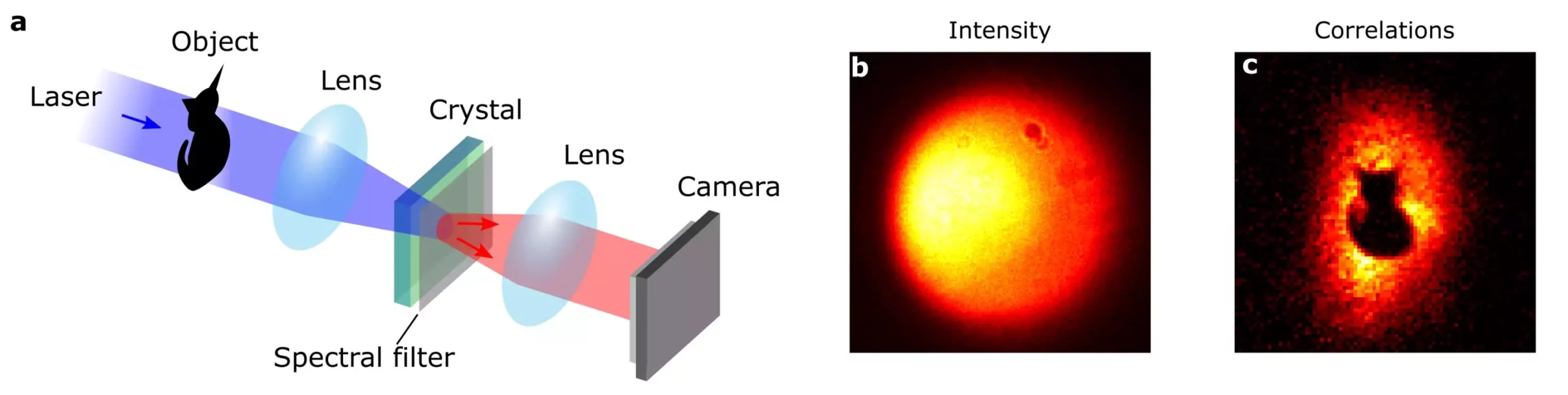
Imagine a revolutionary leap in imaging technology where concealed information can exist in plain sight such that it evades detection by even the most sophisticated cameras. This concept may sound like the premise of a science fiction novel; however, a team from the Paris Institute of Nanoscience at Sorbonne University has turned this imaginative notion into reality. Through innovative use of quantum optics, researchers led by Hugo Defienne have pioneered a technique that utilizes the elusive nature of entangled photons to encode visual data, rendering it invisible to standard imaging systems.
Central to this groundbreaking technique is an intriguing process known as spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC). By directing a high-energy photon, generated by a blue laser, into a nonlinear crystal, the photon is halved, resulting in two lower-energy entangled photons. When an image is projected onto this crystal, a remarkable transformation occurs. In the absence of the crystal, the setup functions like a traditional imaging system, revealing a clear image. However, with the crystal present, what emerges at the camera is startlingly uniform—signifying that the original visual data has vanished from sight, hidden cunningly within the quantum correlations of the entangled photons.
To uncover these hidden images, the research team employed a single-photon sensitive camera coupled with advanced algorithms capable of detecting photon coincidences. Essentially, by taking note of instances where pairs of entangled photons arrive at the detector simultaneously, the researchers can reconstruct the original image. As Defienne aptly summarizes, “The image is transferred into the spatial correlations of the photons.” Conventional approaches to imaging, which rely solely on counting individual photons, would miss the concealed visual content entirely. However, tapping into the quantum properties of light enables the researchers to extract information that remains imperceptible through ordinary methods.
Chloé Vernière, a Ph.D. candidate under Defienne’s guidance and a co-author of the study published in *Physical Review Letters*, emphasizes the flexibility and relative simplicity of this approach. The adaptability of the technique holds promise for various applications in the field. By fine-tuning the characteristics of the laser and the nonlinear crystal, researchers envision the encoding of multiple images within a single beam of entangled photons, opening new avenues for future imaging technologies.
Beyond imaging, the implications of this discovery extend significantly into secure quantum communication. In a world where data privacy is paramount, the ability to encode information in such an obscure manner could enhance secure communications, shielding data from potential interception. Additionally, quantum imaging utilizing this method displays resilience against scattering media such as fog or biological tissues, positioning it as a superior alternative to classical light, especially in challenging environments.
As research progresses, the marriage of quantum mechanics and imaging technology demonstrates vast potential not just for academic exploration but also for practical advancements. The approach opens multiple possibilities—from enhancing surveillance systems to enabling diagnostics in medical imaging, where obscured features might be brought into clearer focus through the uniquely powerful attributes of quantum light.
The work being conducted in Paris not only reshapes our understanding of visual data encoding but also pushes the boundaries of technology into territories previously thought unreachable. The ability to hide images within quantum properties and later extract them underscores both the elegance and complexity of quantum optics, indicating that the future of imaging is not just bright—it is hidden, waiting for those with the right tools to reveal it.