Small electric motors play a crucial yet often underestimated role in our daily lives. From household appliances like refrigerators and washing machines to tools and advanced computer systems, they power countless devices. Notably, in modern automobiles, these motors drive essential auxiliary systems, including pumps and fans. While each individual motor may consume minimal energy, their collective impact opens lucrative avenues for energy savings. There is an urgent need to explore and enhance the efficiencies of these motors, especially as sustainable technology becomes a growing focus on global energy strategies.
A concerted effort from the research team at Graz University of Technology’s Electric Drives and Power Electronic Systems Institute has led to significant advancements in this field. Under the guidance of Annette Mütze, the “CD Laboratory for Brushless Drives for Pump and Fan Applications” has embarked on a mission to explore the potentials of brushless integrated drives. This research not only emphasizes energy efficiency but also addresses noise pollution and weight optimization in motor design.
A notable part of this innovation involves using larger claw pole motors—often associated with vehicle lighting systems—which are less commonly recognized for their application in small drive units. By implementing strategies such as skewing and slotting the claw configurations, the researchers effectively mitigated the cogging torques that typically generate vibrations within the motor. Such techniques incur minimal additional costs while significantly enhancing the motor’s operational smoothness. According to Mütze, the approach taken has reduced one of the main sources of noise by a staggering 70%, making these drives much more appealing for consumers considering quiet operation.
Efficiency in electric motors is critical, especially given the need for sustainable energy consumption. A major innovation introduced by Mütze’s team relates to the motor’s current regulation. Traditional methods often rely on pulse width modulation (PWM), which, while effective, involves numerous switching operations. These operations can inadvertently lead to increased energy consumption due to switching losses.
In contrast, the novel control strategy employed by the Graz research team allows for a significantly reduced number of switching actions. By switching the drives on and off just once per desired operation cycle, this innovative practice leads to lower energy losses. This results in marked efficiency gains, particularly at lower currents, providing an overall superior performance compared to conventional PWM-controlled motors. The impact extends beyond energy savings; the ability to halve the necessary capacitors on the circuit boards translates directly into reduced manufacturing costs.
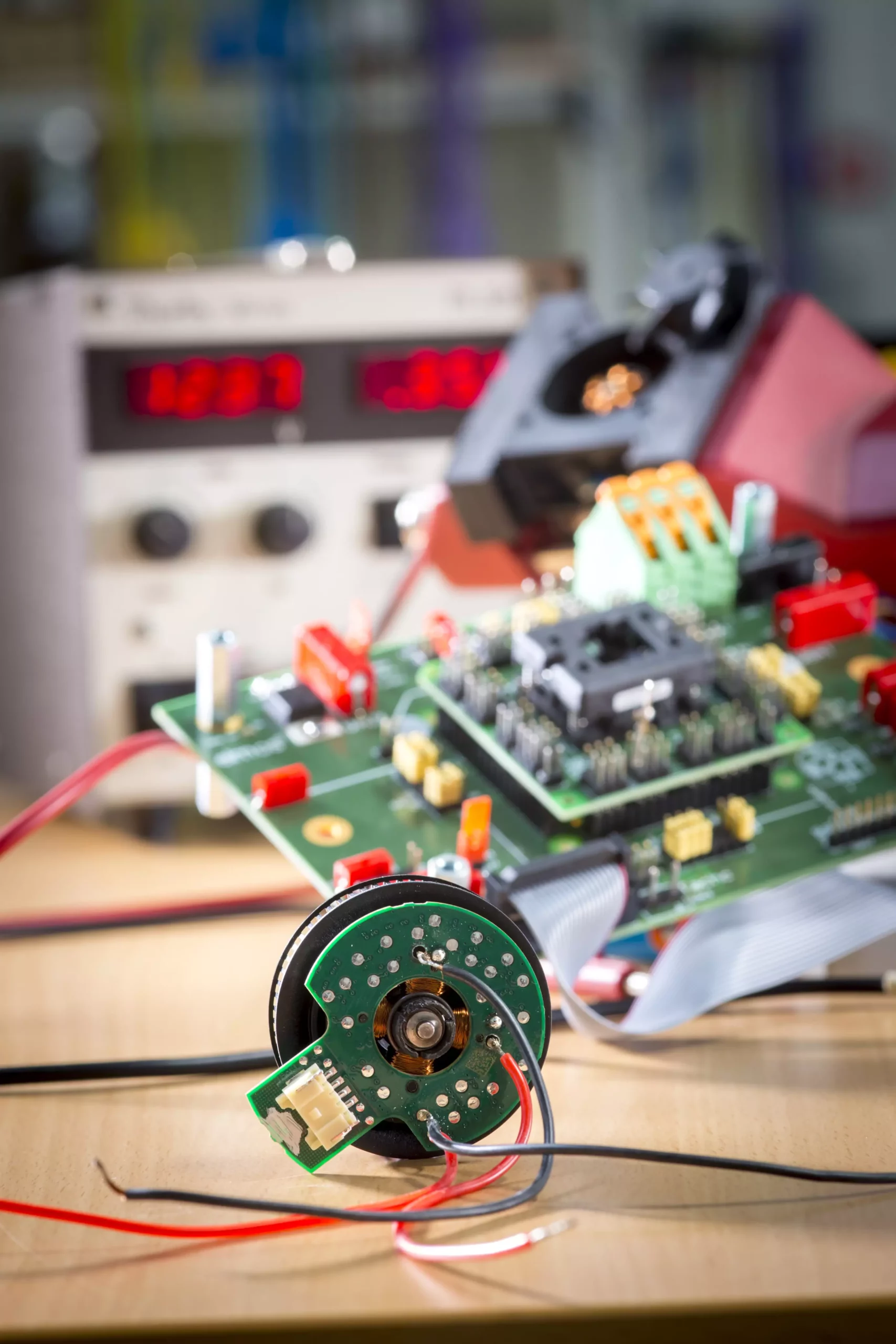
The innovations do not stop at control strategies. The adoption of printed circuit board (PCB) motors with ferrite cores represents another transformative stride in motor technology. The design allows for much of the motor’s components to be integrated seamlessly onto PCBs, promoting higher levels of automation during production processes. Incorporating 3D-printed ferrite cores has led to improvements in the guidance of magnetic flux within the motors, which is vital for overall operational efficiency.
These advancements set the stage for cost-effective magnetic materials. Ferrite-based magnets can be utilized, which are not only less expensive but also provide the necessary performance characteristics for efficient motor operation. This approach is compelling because it balances the need for performance and affordability, making the new motors an attractive option for manufacturers.
The developments spearheaded by Annette Mütze and her team at Graz University of Technology are pioneering efforts to transform the electric motor industry. By focusing on reducing energy consumption, enhancing operational efficiency, and implementing innovative manufacturing processes, there is significant potential for these small electric motors to lead the charge toward more sustainable energy practices. As technology continues to evolve, the newfound efficiencies in small electric motors may very well play a pivotal role in the future landscape of energy consumption, not just in household appliances but across various sectors. Embracing such innovations can drive us closer to a greener, more efficient world.