The surge in solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind energy capacity has become unmistakable over the last few years. As of 2023, these forms of renewable energy have seen their combined capacity more than double since 2018, fundamentally altering the landscape of electricity generation. This growth is bolstered by supportive government policies and a continuous decline in costs. As these renewable resources become ever more pivotal in global energy portfolios, the challenge of integrating them into existing power systems is becoming increasingly acute. The International Energy Agency (IEA) recently published a report, “Integrating Solar and Wind: Global experience and emerging challenges,” highlighting the imperative nature of this transition.
As governments and policymakers champion the advancement of clean energy, the integration of variable renewable energy (VRE) sources into the power grid stands as one of the most formidable barriers. The urgency to ensure a seamless integration into power systems cannot be overstated, particularly given the potential consequences of delays. If appropriate integration measures are not implemented timely, projections indicate that the contribution of solar PV and wind energy could fall short by a significant 15% come 2030. Consequently, the overall share of renewable energy in the global electricity mix could diminish by five percentage points, resulting in a potential loss of environmental and economic benefits.
The IEA report underscores the pressing need for decisive action among policymakers to fully realize the advantages that VRE sources offer. Such action is not merely a matter of ambition; it is essential for meeting global climate commitments and achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century. This requires innovative thinking and the application of measures that have been successful in various jurisdictions around the world.
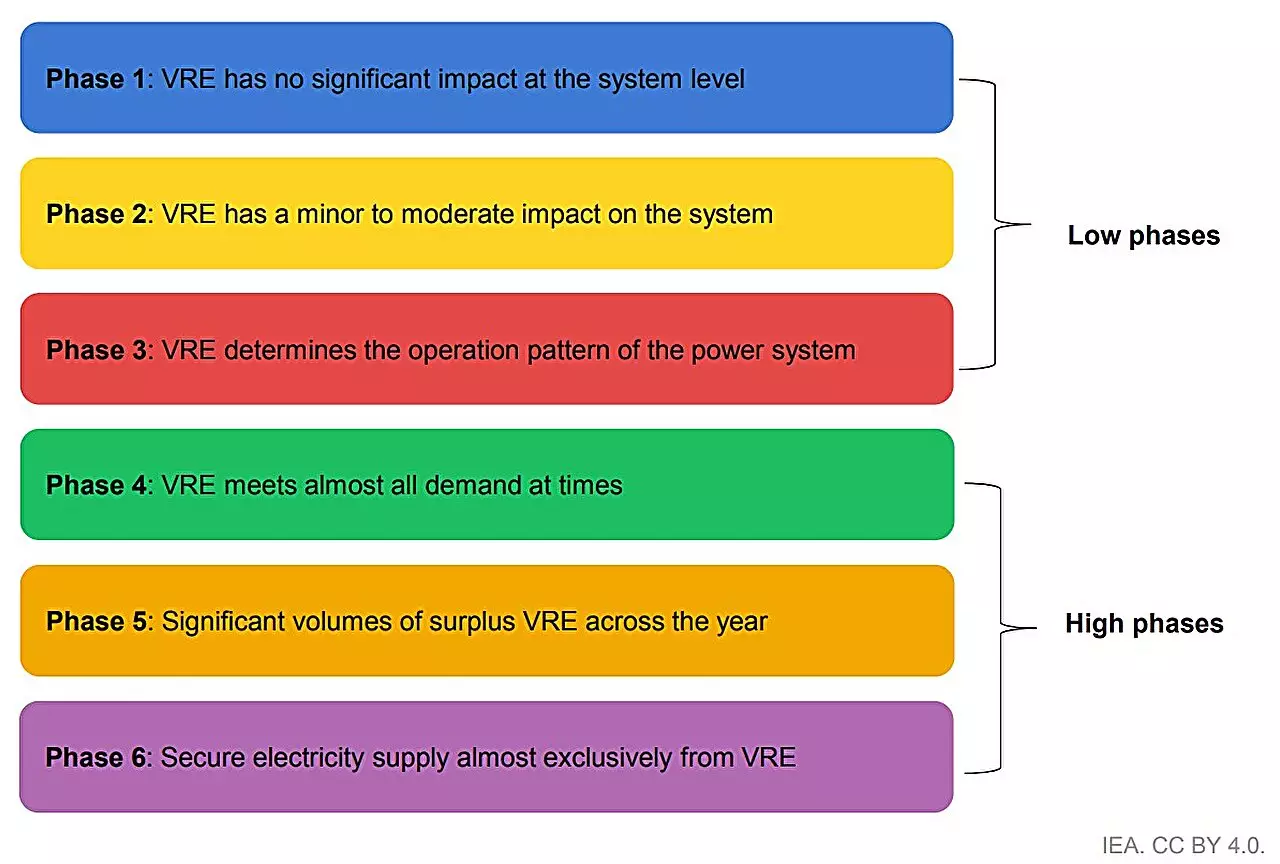
A distinguishing feature of the IEA report is its comprehensive assessment of integration measures implemented across 50 power systems that collectively account for nearly 90% of global solar PV and wind generation. Through this extensive stocktake, the report offers valuable insights into strategies that countries have employed, particularly those currently experiencing low penetration of VRE sources in their energy mixes. Notably, these countries can significantly enhance their renewable deployment without necessitating extensive systemic overhauls.
Proven strategies include improving the operational flexibility of existing energy assets and refining forecasting techniques. These incremental adjustments can effectively accommodate the variability inherent in solar and wind energy, allowing for a more resilient and reliable power system. However, as energy systems continue to evolve, more significant challenges may arise, particularly as VRE penetration levels climb. Consequently, frontrunner countries such as Denmark, Spain, Ireland, and South Australia serve as examples of how proactive policy measures and technological advancements can mitigate these challenges.
Investment in energy storage solutions and the development of innovative power grid technologies play a crucial role in managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. These approaches address the daily and seasonal fluctuations associated with solar and wind energy production, ensuring stability and reliability in electricity supply.
While technological advancements are instrumental in overcoming the challenges of integrating renewables, the IEA report emphasizes that the successful implementation of these solutions often hinges on appropriate policy and regulatory frameworks. Existing technologies aimed at enhancing system stability and flexibility are either mature or approaching maturity. Therefore, the focus must shift towards developing supportive regulations and policies that encourage the integration of VRE into existing infrastructures.
Furthermore, a significant paradigm shift is necessary in how energy systems are traditionally planned and operated. This transition calls for a forward-thinking approach that anticipates and accommodates the growing integration of variable renewables. Policymakers must adopt proactive measures to ensure that energy systems evolve in tandem with the increasing adoption of renewables.
The path towards a sustainable and decarbonized energy future hinges on the effective integration of renewable sources into our power systems. As the adoption of solar PV and wind energy accelerates, addressing the integration challenges effectively will be paramount. The insights provided by the IEA report present a roadmap for countries to harness the full potential of renewable energy, ultimately leading to a cleaner, more secure, and resilient energy future.