As energy consumption continues to rise worldwide, the need for innovative indoor heating solutions becomes increasingly imperative. The conventional heating methods often fall short in terms of efficiency and adaptability, especially in residential spaces where heating demands fluctuate. A recent research publication in the field of engineering has explored a new, promising technology that aims to address these limitations while enhancing thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
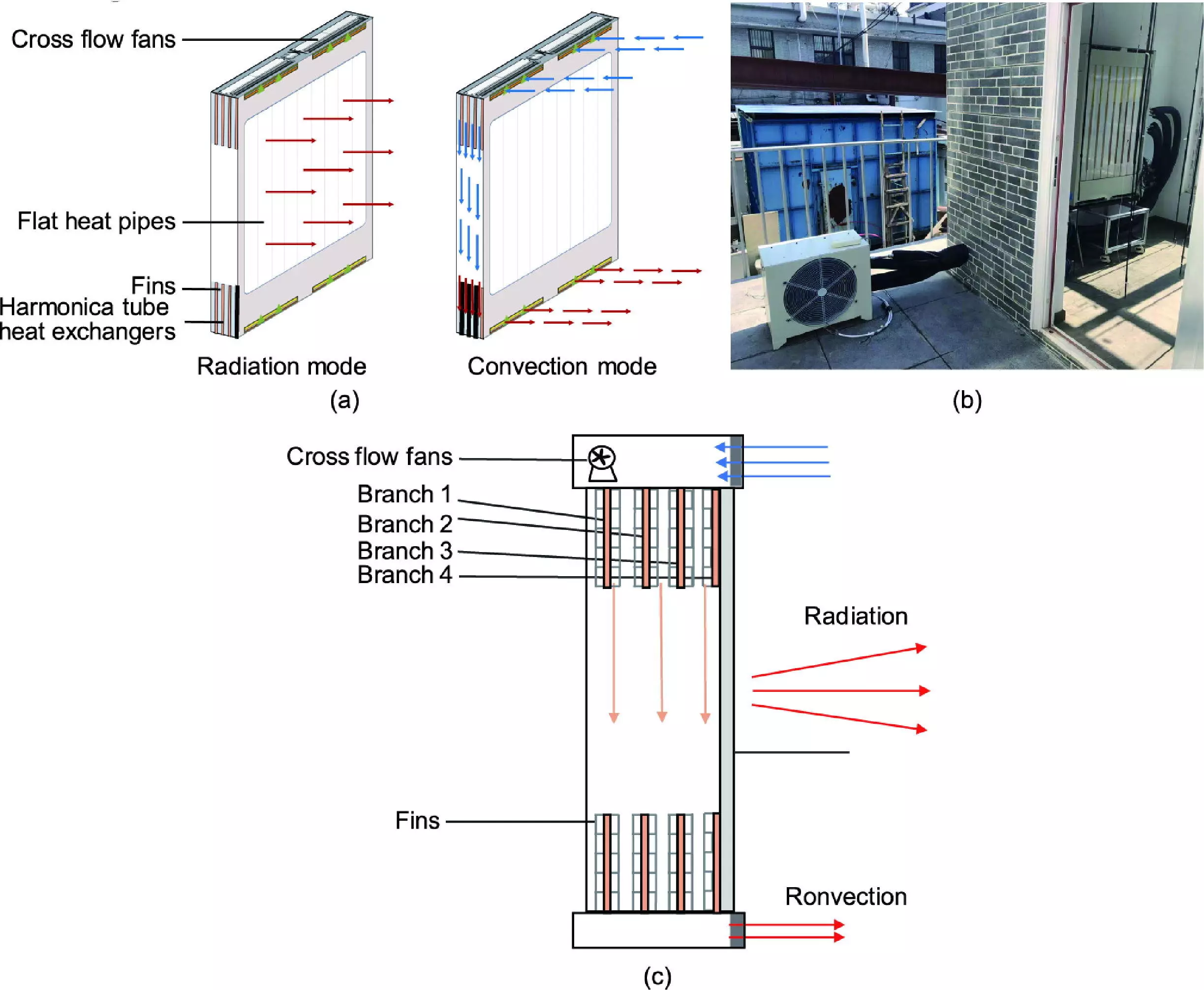
The study, “Indoor Thermal Environment Improvement Based on Switchable Radiation/Convection-Combined Intermittent Heating,” outlines the development of a unique radiant-convective heating terminal designed for intermittent heating purposes. This innovative system combines the principles of both radiant and convective heating, which historically have worked independently, to create a more efficient alternative. Researchers argue that there is untapped potential in intermittent heating, particularly in residential setups where the heating load may vary significantly throughout the day.
Conventional heating terminals often struggle to balance energy efficiency and user comfort. One of the key arguments presented in the study is the inadequacy of existing radiant and convective heating systems to function synergistically. These conventional systems typically either consume excess energy to maintain comfort levels or fail to deliver sufficient heat during cooler periods. This recognition of their shortcomings underscores a critical need for advanced heating solutions capable of adapting to user demands without sacrificing energy efficiency.
Through rigorous experimentation, the researchers demonstrated that their novel heating terminal could effectively warm a standard residential environment in a remarkable 20 to 40 minutes. More impressively, once the target temperature range of 18–22°C was achieved, the system maintained this stable condition. The results illustrated that the new terminal outperformed the previous combination of conventional heating technologies, particularly in its capacity for rapid warm-up times, heating flexibility, and responsive thermal management.
The switchable mode of the radiant-convective terminal adds another layer of efficiency, facilitating seamless transitions between heating modes to meet varying thermal demands. This adaptability leads to significant energy savings while ensuring a comfortable indoor climate.
The study does not only end at presenting a new technology but also hints at future advancements in heating design. By applying the experimental and numerical simulation data obtained during their research, designers of heating systems can explore new configurations that can optimize terminal heat transfer. The potential for a single type of terminal to replace dual conventional systems simplifies heating infrastructure, promising lower costs for both manufacturers and consumers.
The implications of these findings are profound, serving as a valuable reference point for future developments in intermittent heating systems. With a focus on both energy efficiency and user comfort, this research sets the stage for a paradigm shift in how we approach indoor thermal environments.
The innovative switchable radiant-convective heating terminal presents a significant advancement in residential heating technology. As we continue to seek sustainable solutions in energy consumption, this novel approach could redefine our expectations for indoor heating systems, where efficiency does not come at the expense of comfort. With further exploration and development, we may find ourselves warming our homes in an intelligent, economical, and environmentally conscious manner.