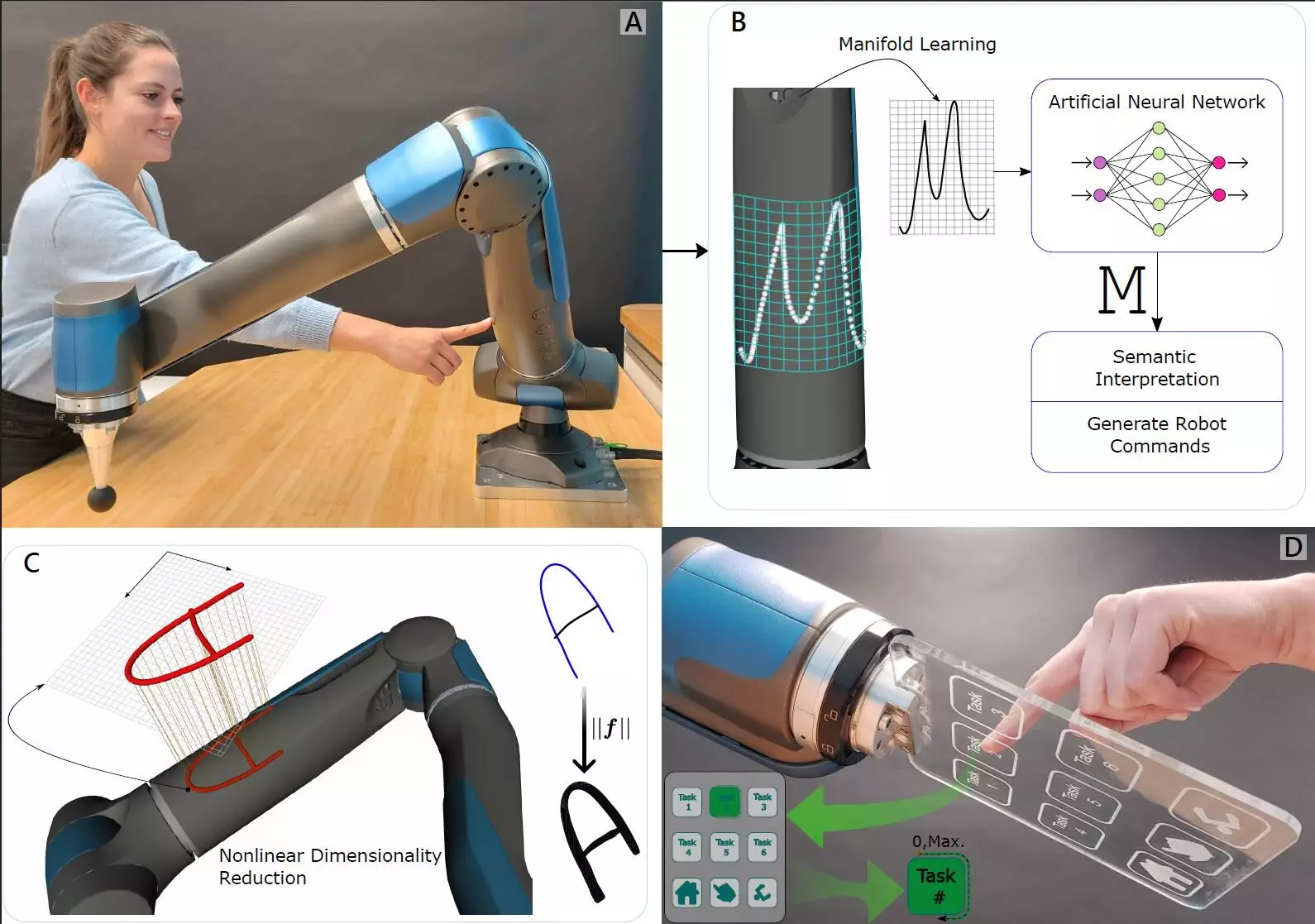
In a groundbreaking study from the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, researchers are challenging traditional perceptions of robotic touch. Unlike previous advancements that relied heavily on artificial skin technology, this study emphasizes a more sophisticated internal mechanism combined with machine learning to give robots a nuanced sense of touch. This innovative approach holds tremendous potential for enhancing human-robot interactions, especially in industrial settings where precision and safety are paramount.
Understanding Touch: A Dual Perspective
Touch is more than just a simple sensory experience; it operates on a dual pathway. Living beings can both give and receive tactile feedback, resulting in a dynamic engagement with their environment. Historically, robots have struggled to replicate this complex interaction. However, the research team has tackled this challenge head-on. By integrating traditional internal force-torque sensors with advanced machine learning techniques, they have created a system that captures both the act of touching and being touched. This paradigm shift not only improves robot functionality but also provides foundational insights into how robots can interpret external stimuli in a human-like manner, delivering a more immersive and interactive experience.
Transformative Technology: The Combination of Sensors and Algorithms
The pivotal innovation of this study centers around the application of force-torque sensors embedded within the joints of a robotic arm. These sensors are finely tuned to detect pressure from multiple angles, which enhances their ability to perceive various types of touch. When combined with sophisticated machine learning algorithms, the robot not only learns to sense touch but also to interpret these sensations in a meaningful way. For instance, the research revealed that the robotic arm could distinguish itself when prompted by subtle variations in touch, such as identifying a specific digit drawn on its surface. This ability to differentiate sensory input is groundbreaking, suggesting a future where robots can interact on a more human-like level.
Implications for Human-Robot Collaboration
The implications of this technology cannot be overstated. As robots become more prevalent in industries that require close human interaction, such as manufacturing or healthcare, the ability to recognize and respond appropriately to touch will foster a safer and more efficient working environment. Automated systems that can interpret tactile feedback will make bots more intuitive collaborators, alleviating concerns about safety and increasing operational harmony between humans and machines.
Moreover, as robots gain the ability to ‘feel’ their interactions, we can expect an evolution in how we view robots overall. This shift toward tactile awareness may culminate in new opportunities for robots to engage in environments where human presence is vital—be it assisting in hospitals or working alongside humans on production lines.
The path to this robotic sensitivity reveals an essential truth: the future of robotics is intricately linked to our understanding of sensory interaction. By pushing the boundaries of technology and design, we can forge a partnership between humans and robots that enhances not just productivity but the quality of interpersonal relationships in our increasingly automated world.