Tidal energy stands on the brink of a major breakthrough along the UK coastline, with projections indicating a significant increase in offshore renewable energy installations in the forthcoming decades. This burgeoning interest in tidal energy as a source of clean power heightens awareness of the complexities involved in deploying advanced devices like tidal turbines in turbulent marine environments. These complexities not only include the performance of the turbines but also the broader ecological impacts on marine life and habitats.
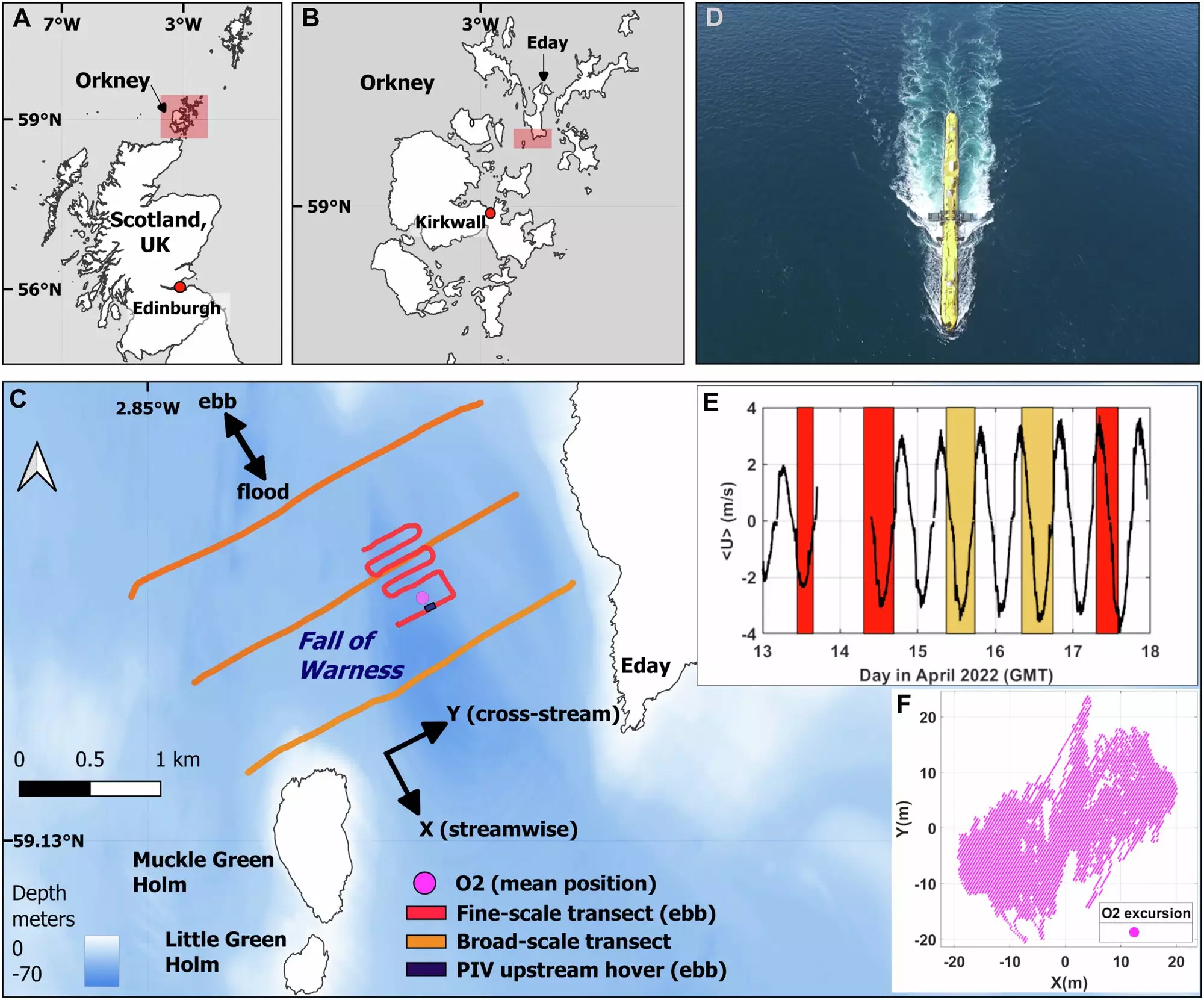
At the forefront of tidal energy innovation is Orbital Marine Power’s O2 turbine, strategically positioned in the powerful tidal currents of the Orkney Islands, Scotland. This remarkable device diverges from traditional models, as it floats on the sea surface rather than being fixed to the seabed. With a length exceeding 70 meters and the potential to supply electricity to around 2,000 households annually, the O2 represents a significant leap in tidal energy technology. Its unique design allows it to harness the kinetic energy of fast-moving water—an asset, given that water’s density allows for more efficient energy production than wind energy systems of equivalent size.
However, embarking on tidal energy exploitation is riddled with complications. A recent study harnessed aerial drone technology along with boat-based surveys to closely examine the tidal flows encountered by the O2. The findings underscored the challenges presented by tidal flows exceeding speeds of 8 knots, impacting both the operational efficacy of the turbine and its interaction with other marine organisms and installations. With tidal energy’s potential to contribute up to 11% of the UK’s electricity needs, understanding these challenges, particularly how turbine wake can influence the positioning of future installations and local ecosystems, is crucial.
Notably, the research conducted by a collaboration of institutions—including the Marine Biological Association and the University of Plymouth—has illuminated important insights. The team emphasized the necessity of site-specific assessments prior to the installation of tidal turbines. This highlights the urgency of integrating empirical data with simulations to enhance the strategic placement of turbines in ecologically sensitive areas.
A previous study led by the same group of researchers found that the turbine’s wake could serve as a consistent feeding ground for nearby seabirds. However, there are dangers associated with tightly clustered turbine arrays, as they may obstruct the natural movement of marine fauna, including vital predator species like orcas. This importance of evaluating the ecological ramifications of tidal energy installations cannot be overstated and forms a key aspect of future research endeavors.
The innovative use of drone technology in conducting oceanographic surveys within these dynamic tidal environments exemplifies how scientific expertise can be augmented through technological advancements. The combination of detailed aerial mapping and direct marine observation provides a comprehensive understanding of tidal dynamics, thus empowering researchers to address the challenges posed by variable marine conditions. As Dr. Lilian Lieber, senior research fellow, articulated, navigating the complexities of placing turbines in multi-faceted marine landscapes is paramount for optimizing energy output while safeguarding marine environments.
Despite the promising horizon for tidal energy, several significant hurdles remain. The costs of scaling up tidal technology, ensuring its long-term reliability in tumultuous conditions, and navigating technical limitations related to grid capacity are among the most pressing issues. As more offshore renewable energy infrastructures spring up, scientists and engineers must work in tandem to mitigate these challenges.
The research published in *Nature Communications* signifies not just a step forward in understanding tidal flows, but also a commitment to sustainable development in energy generation. A thorough understanding of local conditions is essential for fostering successful tidal energy projects—the research underscores that empirical studies combined with real-world assessments are indispensable tools in the quest for reliable renewable energy solutions.
The expansion of the tidal energy sector coincides with a global shift towards cleaner energy sources. As renewable installations increase along the extensive UK coastline, the confluence of research, technology, and environmental awareness will be critical in paving the way for a sustainable energy future. The insights garnered from studies like these will not only aid in optimizing the operational efficiency of tidal turbines but also enhance our understanding of how such technologies can coexist with marine ecosystems, ultimately ensuring that the benefits of tidal energy can be realized without compromising the health of our oceans.